How to Create the Perfect Autumn Hiking Fits: A Layering Masterclass
When the leaves begin their spectacular transformation and crisp morning air signals autumn’s arrival, experienced hikers know that mastering the art of layering becomes absolutely crucial for outdoor comfort and safety. How to Create the Perfect Autumn Hiking Fits: A Layering Masterclass isn’t just about looking good on the trail—it’s about creating a versatile clothing system that adapts to autumn’s unpredictable weather patterns, from frosty dawn starts to surprisingly warm afternoon sun. 🍂

The secret lies in understanding how different fabric technologies work together to create a microclimate around your body, regulating temperature and moisture while providing protection from wind, rain, and sudden weather changes that make autumn hiking both thrilling and challenging.
Key Takeaways
- The three-layer system (base, insulating, outer shell) forms the foundation of effective autumn hiking attire
- Fabric choice matters more than brand names—prioritize moisture-wicking, breathable, and quick-drying materials
- Temperature fluctuations in autumn require easily adjustable layers that can be added or removed quickly
- Weather versatility is essential—prepare for rain, wind, temperature drops, and unexpected sunshine
- Proper fit and mobility ensure comfort during long hikes while maintaining thermal efficiency
Understanding Autumn’s Unique Hiking Challenges
Autumn presents hikers with a complex set of environmental variables that make clothing selection particularly challenging. Unlike summer’s consistent heat or winter’s predictable cold, autumn weather creates a perfect storm of conditions that demand strategic preparation.
Temperature Swings and Microclimate Variations
Fall hiking often begins in near-freezing temperatures at dawn, progresses through comfortable mid-morning conditions, peaks with surprisingly warm afternoon sun, and concludes with rapidly dropping temperatures as daylight fades. These dramatic temperature swings, sometimes spanning 30-40 degrees Fahrenheit in a single day, require a clothing system that adapts seamlessly.
Elevation changes compound these challenges. For every 1,000 feet of elevation gain, temperatures typically drop 3-5 degrees Fahrenheit. A hike that starts at a comfortable 55°F trailhead can reach summit conditions of 35°F or lower, especially when combined with wind chill effects.
Moisture Management Complexities
Autumn introduces multiple moisture sources that hikers must navigate:
- Morning dew and frost that saturates vegetation
- Intermittent rain showers common during seasonal transitions
- Internal moisture from exertion during temperature fluctuations
- Snow at higher elevations that can melt and refreeze
- Stream crossings with higher water levels from fall precipitation
“The key to autumn hiking comfort isn’t staying completely dry—it’s managing moisture effectively while maintaining core body temperature.” – Outdoor Gear Expert
The Science Behind Effective Layering Systems
Understanding How to Create the Perfect Autumn Hiking Fits: A Layering Masterclass requires grasping the scientific principles that make layering systems work effectively. Each layer serves a specific physiological function in maintaining optimal body temperature and comfort.
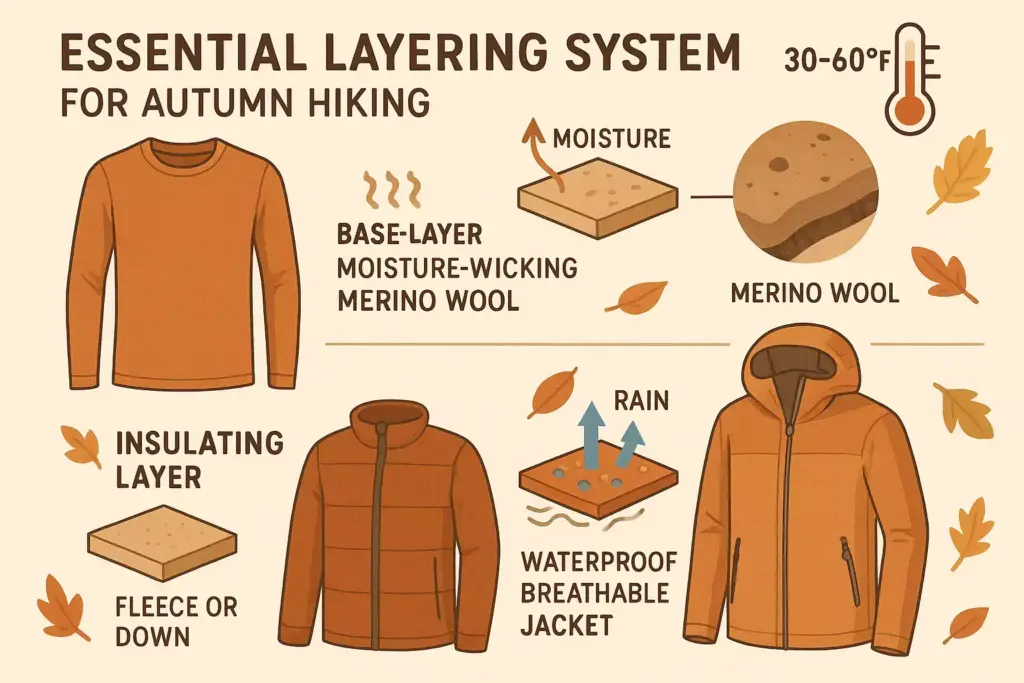
Base Layer: The Moisture Management Foundation
The base layer functions as your second skin, directly managing the moisture your body produces during physical exertion. Quality base layers utilize advanced fabric technologies to:
Wick moisture away from skin through capillary action, moving sweat to the fabric’s outer surface where it can evaporate more efficiently. This process prevents the cooling effect of wet clothing against skin, which can lead to hypothermia in cool autumn conditions.
Regulate skin temperature through fabric weight and construction. Lightweight base layers work well for high-output activities, while midweight options provide additional warmth during lower-intensity hiking or rest stops.
Provide antimicrobial properties that prevent odor buildup during multi-day adventures. Merino wool naturally resists bacterial growth, while synthetic fabrics often incorporate silver ion treatments for similar effects.
Insulating Layer: Thermal Regulation Control
The insulating layer creates dead air space around your body, trapping warm air while allowing moisture to continue moving outward. This layer provides the primary warmth regulation in your layering system.
Down insulation offers exceptional warmth-to-weight ratios and compressibility, making it ideal for dry autumn conditions. However, down loses insulating properties when wet, requiring careful consideration of weather conditions.
Synthetic insulation maintains warmth when damp and dries quickly, making it more versatile for unpredictable autumn weather. Modern synthetic fills like PrimaLoft and Climashield approach down’s performance while offering superior wet-weather reliability.
Fleece and wool options provide excellent breathability and moisture management, perfect for high-output activities where temperature regulation requires frequent adjustments.
Outer Shell: Environmental Protection Barrier
The outer shell serves as your first line of defense against external elements while allowing internal moisture to escape. Advanced shell technologies balance waterproof protection with breathability.
Waterproof-breathable membranes like Gore-Tex, eVent, and proprietary technologies create microscopic pores that allow water vapor to escape while preventing liquid water from entering.
DWR (Durable Water Repellent) coatings on the shell’s exterior cause water to bead and roll off, preventing fabric saturation that would compromise breathability.
Ventilation features including pit zips, chest vents, and back vents allow rapid heat and moisture release during high-exertion periods.
🍂 Autumn Hiking Layer Calculator
Essential Fabric Technologies for Autumn Hiking
How to Create the Perfect Autumn Hiking Fits: A Layering Masterclass depends heavily on selecting fabrics that perform reliably in autumn’s challenging conditions. Understanding fabric technologies helps hikers make informed decisions that directly impact comfort and safety.
Merino Wool: Nature’s Performance Fabric
Merino wool stands out as the gold standard for autumn hiking base layers, offering unique properties that synthetic alternatives struggle to match completely.
Temperature regulation occurs naturally through merino wool’s crimped fiber structure, which traps air for insulation while allowing excess heat to escape. This self-regulating property makes merino ideal for autumn’s temperature fluctuations.
Odor resistance comes from wool’s natural antimicrobial properties, allowing hikers to wear the same base layer for multiple days without developing unpleasant odors—crucial for multi-day autumn adventures.
Moisture management in merino wool works differently than synthetic fabrics. Wool can absorb up to 30% of its weight in moisture while still feeling dry against the skin, then releases that moisture gradually as conditions change.
Advanced Synthetic Technologies
Modern synthetic fabrics offer specific advantages that complement or sometimes exceed natural fibers in autumn conditions.
Polyester blends with advanced weave structures provide excellent moisture wicking and quick-drying properties. Brands like Patagonia’s Capilene and Arc’teryx’s Phasic series utilize specialized polyester constructions for enhanced performance.
Nylon components add durability and stretch, important for maintaining fabric integrity during extended autumn hiking seasons with varied terrain and vegetation contact.
Polypropylene bases offer superior moisture wicking but require careful attention to odor management through antimicrobial treatments or frequent washing.
Hybrid Fabric Systems
Wool-synthetic blends combine the best properties of both fiber types, offering improved durability over pure wool while maintaining much of wool’s natural performance characteristics.
Zone construction places different fabric types in specific areas—merino wool in odor-prone zones, synthetic materials in high-abrasion areas, and mesh panels for enhanced ventilation.
Building Your Autumn Layering System: A Complete Guide
Creating the perfect autumn hiking outfit requires understanding how to combine layers effectively for maximum versatility and performance. How to Create the Perfect Autumn Hiking Fits: A Layering Masterclass involves strategic selection and coordination of each system component.
Base Layer Selection and Fit
Proper base layer fit should be snug but not restrictive, allowing full range of motion while maintaining contact with skin for effective moisture transfer. Avoid loose-fitting base layers that create air gaps and reduce thermal efficiency.
Weight categories determine base layer performance:
- Lightweight (150-200 gsm): Ideal for high-output activities and temperatures above 40°F
- Midweight (200-250 gsm): Versatile choice for most autumn conditions and moderate activity levels
- Heavyweight (250+ gsm): Best for cold mornings, low activity levels, or as a standalone layer
Seam construction affects comfort during long hiking days. Flatlock seams reduce chafing, while merrow seams provide durability without bulk.
Insulating Layer Strategies
Layering flexibility requires choosing insulating pieces that work well together and can be easily adjusted as conditions change.
Vest options provide core warmth while allowing arm mobility and heat release, perfect for autumn hiking where upper body temperature regulation is critical.
Full jacket systems offer comprehensive warmth but require ventilation features like pit zips to prevent overheating during ascents.
Hybrid insulation combines different insulation types in strategic zones—down in the core for maximum warmth, synthetic in moisture-prone areas for reliability.
Shell Layer Coordination
Breathability ratings become crucial in autumn when internal heat production varies significantly throughout the day. Look for shells with breathability ratings above 15,000 g/m²/24hr for active use.
Ventilation systems should include multiple options:
- Pit zips for rapid heat release during climbs
- Chest vents for fine-tuning airflow
- Back vents for continuous heat release
- Hem adjustments to control airflow at the waist
Layering compatibility ensures your shell accommodates all intended insulating layers without restriction while maintaining weather protection.
Seasonal Transition Considerations

Autumn hiking presents unique challenges as weather patterns shift and daylight hours decrease. Successful autumn layering systems must account for these seasonal transition factors.
Early Autumn (September-October)
Temperature variability reaches its peak during early autumn, with potential 40-degree swings between dawn and afternoon temperatures. This period demands maximum layering flexibility.
Insect protection remains important in many regions, requiring base layers that provide coverage while managing increased perspiration from bug-proofing clothing.
Extended daylight allows for longer hiking days but creates greater temperature variation exposure, demanding versatile layering systems.
Late Autumn (November-December)
Shorter daylight hours mean more hiking in cold conditions, shifting layer priorities toward warmth retention rather than heat release.
Precipitation changes from rain to snow require shell layers capable of handling both liquid and frozen precipitation effectively.
Ground conditions become more challenging with frost, ice, and snow, affecting clothing choices for safety and comfort during falls or ground contact.
Regional Variations
Coastal autumn hiking involves higher humidity and more precipitation, favoring synthetic insulation and enhanced breathability.
Mountain autumn conditions create extreme temperature and weather variations with elevation, requiring comprehensive layering systems.
Desert autumn hiking still involves significant heat during midday, but with rapid cooling after sunset, demanding layers that transition quickly.
Advanced Layering Techniques and Pro Tips
Mastering How to Create the Perfect Autumn Hiking Fits: A Layering Masterclass involves understanding advanced techniques that experienced hikers use to optimize their clothing systems.
Dynamic Layering Management
Anticipatory layering involves adjusting layers before you feel too hot or cold, preventing the discomfort and energy loss associated with temperature extremes.
Microclimate awareness helps hikers recognize when terrain features like valleys, ridges, or forest canopies will affect temperature and adjust layers accordingly.
Activity-based adjustments require understanding how different hiking activities (steep climbs, flat sections, rest stops) affect heat production and planning layer changes accordingly.
Ventilation Optimization
Progressive ventilation starts with small adjustments (opening pit zips) before removing entire layers, maintaining overall system integrity while fine-tuning comfort.
Strategic layer removal prioritizes removing insulating layers over base or shell layers to maintain moisture management and weather protection.
Timing considerations account for upcoming terrain and weather changes when deciding whether to add or remove layers.
Emergency Preparedness
Redundant warmth systems ensure that if one layer becomes compromised (wet, torn, lost), backup options maintain safety margins.
Rapid deployment capability requires practicing layer changes with gloves on and in poor visibility conditions common during autumn weather changes.
Group coordination involves planning layer systems that work for different group members’ needs and ensuring shared emergency resources.
Common Autumn Layering Mistakes to Avoid
Even experienced hikers make layering errors that compromise comfort and safety during autumn adventures. Understanding these common mistakes helps create more effective clothing systems.
Overdressing at the Start
Starting too warm leads to excessive sweating, which saturates base layers and reduces their insulating effectiveness throughout the day. The general rule suggests feeling slightly cool at the trailhead, knowing that movement will generate warmth within 10-15 minutes.
Cotton base layers remain one of the most dangerous mistakes in autumn hiking. Cotton retains moisture, loses insulating properties when wet, and takes excessive time to dry—potentially life-threatening in cool autumn conditions.
Ignoring weather forecasts or failing to check conditions at different elevations can leave hikers unprepared for sudden weather changes common during autumn.
Poor Layer Coordination
Incompatible layer combinations occur when different pieces don’t work well together—such as bulky insulating layers under tight shells, or base layers that don’t extend properly under other garments.
Neglecting extremities while focusing on core layering can lead to cold hands, feet, and heads that force the body to work harder to maintain core temperature, reducing overall system efficiency.
Inadequate backup planning leaves hikers vulnerable when primary layers become wet, damaged, or lost during the hike.
Fabric Care and Maintenance Issues
DWR coating degradation on shell layers reduces water repellency, causing fabric saturation that compromises breathability and increases weight.
Improper washing techniques can damage technical fabrics, reduce their performance characteristics, and shorten their useful life.
Inadequate drying between uses, especially for natural fibers like wool, can lead to odor issues and reduced performance.
Conclusion: Mastering Your Autumn Hiking Wardrobe
How to Create the Perfect Autumn Hiking Fits: A Layering Masterclass requires understanding the complex interplay between fabric technologies, weather conditions, and personal physiology. Success comes from building a flexible system rather than relying on individual garments, no matter how advanced their technology.
The foundation of effective autumn layering lies in strategic fabric selection—choosing materials that work synergistically to manage moisture, regulate temperature, and provide weather protection. Merino wool base layers, versatile insulating options, and breathable shell systems create the framework for comfort across autumn’s diverse conditions.
Practice and refinement transform theoretical knowledge into practical skill. Test your layering systems during short hikes before committing to longer adventures. Pay attention to how your body responds to different combinations and adjust accordingly.
Your Next Steps
- Assess your current gear against the principles outlined in this guide, identifying gaps or incompatibilities in your layering system
- Test new combinations during short local hikes to understand how different layers work together in real conditions
- Document what works for your body type, activity level, and local climate conditions
- Invest strategically in key pieces that will improve your overall system performance
- Plan for conditions by checking weather forecasts and trail conditions before each autumn adventure
The investment in mastering autumn layering pays dividends in comfort, safety, and enjoyment throughout the hiking season. With proper preparation and understanding, autumn’s challenging conditions become opportunities to experience some of the year’s most spectacular outdoor adventures. 🥾
Remember that perfect layering systems evolve with experience, changing conditions, and gear improvements. Stay curious, keep learning, and enjoy the process of optimizing your autumn hiking experience through thoughtful layering choices.






